Overview and Motivation
Resuable rockets pose an incredibly complex landing sequence problem. For this project I worked with another graduate student and this porject really focuses on the final stage of landing and the objective here is to use applied optimal control strategies for this application is to minimize the fuel consumed.
- Languages: MATLAB, Python
- Framework: ACADO Toolkit
- Skills : Optimal, Nonlinear Dynamics
Approach
Since an elaborate dynamical model of the rocket is extremely complex, we start with a basic 2 DOF dynamic model. In this system, we have for states the position, \([x,\ y]\), velocity, \((v)\), mass, \((m)\) and the control input, \([u_{T},\ u_{\theta}]\) is the thrust and the angle of attack.
Constraints were put on the control inputs, velocity, mass and the angle of attack. Boundary conditions were specified for the final positions and angle of attack, initial velovity and angle of attack(AOA). Optimization problem was solved by using final mass as the Mayer Term in ACADO through MATLAB interface.
Once the convergence was met, this was extended to a 3-DOF system. Since the problem has both path and control constraints, Sequential Quadractic Programming(SQP) was used to solve this Nonlinear Programming(NLP) problem.
Result
| Rocket velocities |
Convergence for the 3-DOF problem |
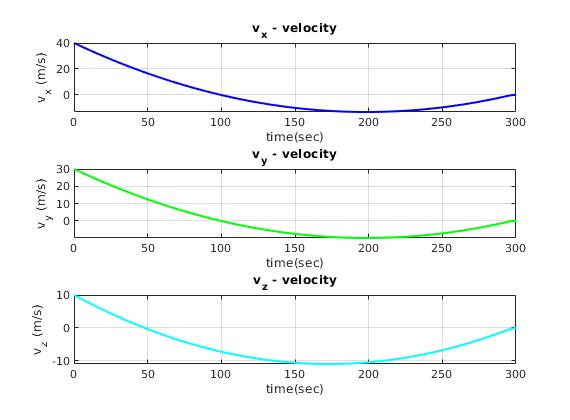 |
 |
Challenges
- The intial position, integration tolerance and tight constraints played a significant role in the convergence of the NLP problem. This was particularly challenging because of the control constraints on thurst, AOA, mass and velocities.
- This project does not address the dynamics of pitch angle and heading angle.